what is a good profit margin for food
When it comes to the food industry, profit margin is a crucial metric that determines the financial success of a business.Understanding what constitutes a good profit margin for food establishments is essential for owners and operators.
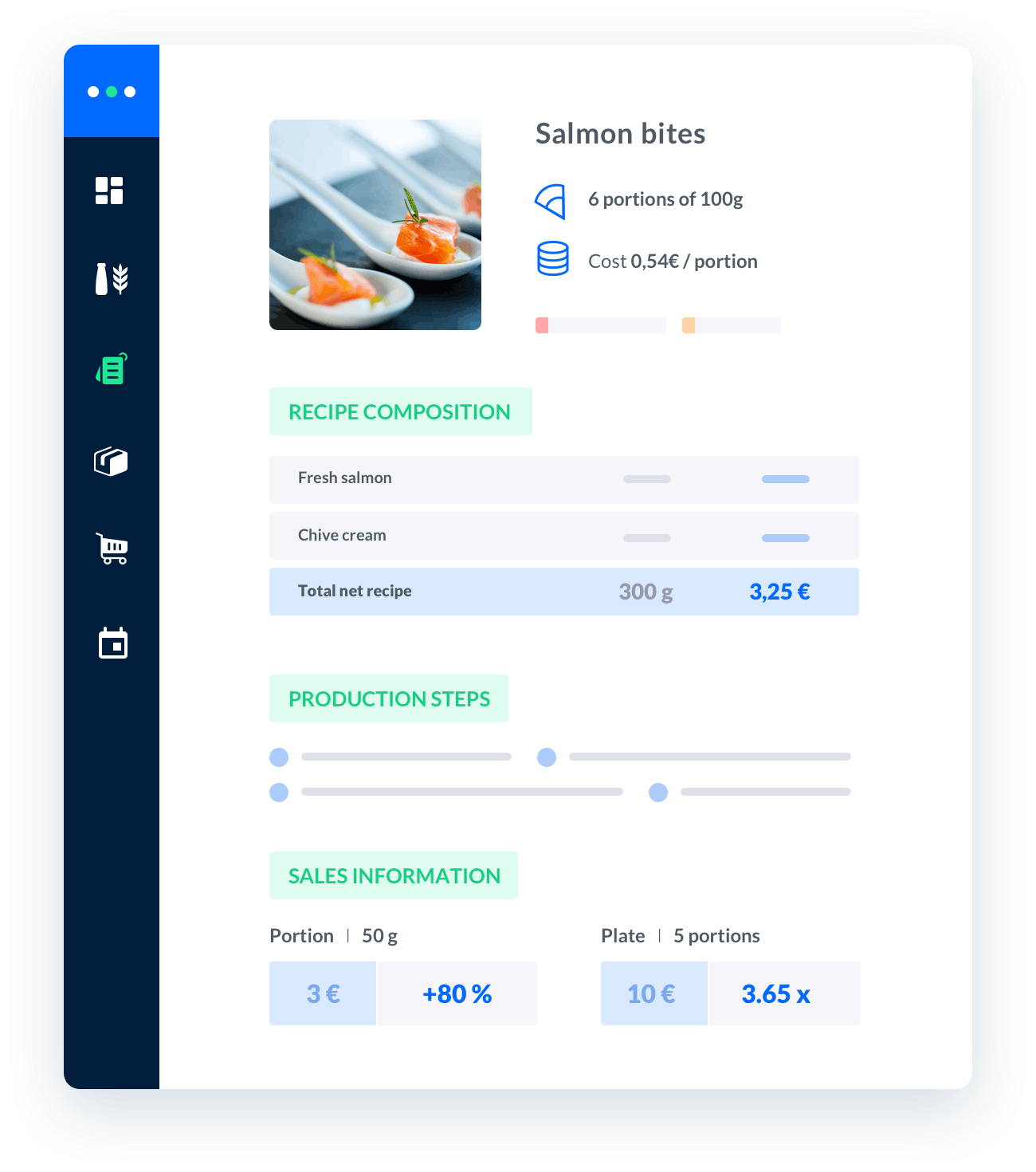
Melba: the food cost app to optimize the profitability of your restaurant
Discover how to optimize the profitability of your restaurant with melba

The ultimate guide to food cost restaurant
Learn more about the food cost basis and how to reduce your food cost percentage
When it comes to the food industry, profit margin is a crucial metric that determines the financial success of a business. Understanding what constitutes a good profit margin for food establishments is essential for owners and operators. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the factors that influence profit margins in the food industry and provide insights on what can be considered a good profit margin.
Factors Influencing Profit Margins in the Food Industry
Several factors play a significant role in determining the profit margins of food businesses. It is important to consider these factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of what constitutes a good profit margin in the food industry:
1. Cost of Ingredients and Raw Materials
The cost of ingredients and raw materials directly impacts the profit margins of food establishments. Sourcing high-quality ingredients at favorable prices can help businesses maintain a healthy profit margin. Efficient inventory management and strategic supplier partnerships can be effective in minimizing ingredient costs.
2. Labor and Operational Costs
Labor and operational costs are another significant factor influencing profit margins in the food industry. Managing wages, benefits, and other operational expenses is crucial to maintaining a good profit margin. Streamlining processes and optimizing labor costs can help businesses improve their bottom line.
3. Pricing Strategy
Setting appropriate prices for menu items is vital for achieving a good profit margin. Pricing too high might deter customers, while pricing too low may lead to unsustainable profit margins. Conducting market research, evaluating competitors' pricing, and analyzing customer preferences can assist in developing an effective pricing strategy.
4. Overhead Costs
Overhead costs, including rent, utilities, insurance, and marketing expenses, impact profit margins. Careful management of these costs can contribute significantly to a good profit margin. Negotiating favorable lease terms, implementing energy-saving measures, and utilizing cost-effective marketing channels are some strategies to control overhead expenses.
What is Considered a Good Profit Margin for Food Establishments?
While profit margins can vary based on various factors, a good profit margin for food establishments is generally considered to be around 5% to 10%. However, it is important to note that profit margins can differ significantly between different types of food businesses.
1. Quick-Service Restaurants (QSR)
Quick-service restaurants, often referred to as fast-food chains, typically operate with lower profit margins due to their competitive pricing strategies and high operating costs. A good profit margin for QSRs ranges between 2% and 6%. These establishments primarily focus on high-volume sales to compensate for lower profit margins.
2. Full-Service Restaurants
Full-service restaurants, which offer table service and a more extensive menu, tend to have higher profit margins compared to QSRs. A good profit margin for full-service restaurants generally falls within the range of 10% to 15%. These establishments can leverage higher menu prices and additional services, such as catering and private events, to increase their profit margins.
3. Specialty Food Stores
Specialty food stores, including gourmet markets and specialty bakeries, often have higher profit margins due to their focus on unique and high-quality products. A good profit margin for specialty food stores can range from 15% to 20%. These establishments cater to niche markets and can charge premium prices for their specialized offerings.
Strategies to Improve Profit Margins in the Food Industry
To achieve and maintain a good profit margin in the food industry, businesses can implement several strategies:
1. Menu Engineering
Conducting an in-depth analysis of menu items' profitability and popularity can help identify opportunities for improvement. Menu engineering involves strategically placing high-profit items, eliminating underperforming dishes, and adjusting prices to optimize profit margins.
2. Efficient Inventory Management
Implementing an effective inventory management system can minimize waste, control costs, and prevent overstocking. By closely monitoring ingredient usage and implementing just-in-time inventory practices, businesses can reduce expenses and improve profit margins.
3. Streamlined Operations
Optimizing operational processes, such as food preparation, order taking, and table turnover, can lead to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. Streamlining operations helps businesses maximize productivity and ultimately improve profit margins.
4. Customer Relationship Management
Building strong relationships with customers through loyalty programs, personalized marketing campaigns, and exceptional customer service can drive repeat business and increase profitability. Satisfied and loyal customers are more likely to choose your establishment over competitors, contributing to improved profit margins.
By considering these strategies and monitoring key financial metrics, food establishments can strive for a good profit margin while delivering exceptional culinary experiences to their customers.






